How to Read DMARC Reports in 2024?

In today’s digital communication DMARC Reports landscape, securing your email channels is essential. Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC Reports) is a crucial protocol that protects your domain from threats like Business Email Compromise (BEC), domain impersonation, and email fraud. Additionally, it offers valuable visibility into your email activities, ensuring that your emails reach their intended recipients while blocking unauthorized senders.
Understanding DMARC Reports
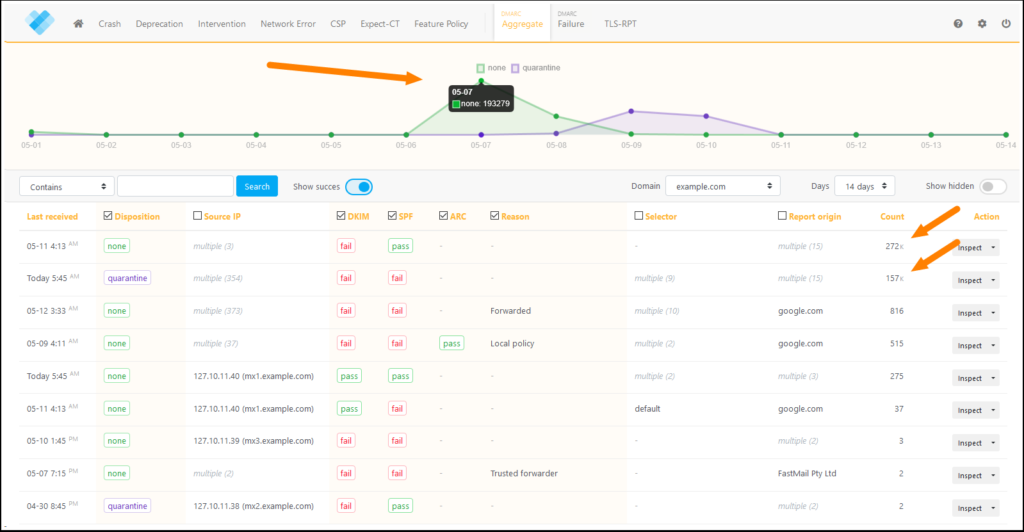
DMARC reports can be intricate and may seem overwhelming at first glance. However, grasping their structure is vital for maintaining strong email security. These reports enable you to review authentication results for every email sent on behalf of your domain, providing insights that can enhance your email strategy.
Key Components of DMARC Reports
DMARC reports contain essential data that help evaluate the effectiveness of your email authentication measures. Key elements include:
- Authentication Results: Information on which emails failed authentication checks and the reasons behind these failures.
- ESP Information: Details about the Email Service Providers (ESPs) that sent the emails.
- Sending IP Addresses: Data on the IP addresses used to send emails, aiding in identifying unauthorized senders.
- Policy Actions: Information on actions taken based on your DMARC policy, such as quarantine or reject.
DMARC reporting is available in two main formats: aggregate reports, which provide an overview of email traffic and authentication status, and failure reports, which detail specific failed authentication attempts.
Enhancing Client Reach Through Visibility in 2024
As we approach 2024, the visibility gained from implementing DMARC can significantly boost your client reach. Here are three primary benefits:
- Improved Site Performance and User Experience: Enhanced visibility into your email authentication data allows for quick identification and resolution of issues, leading to faster, error-free automated emails and improved communication performance.
- Enhanced User Engagement: Properly authenticated emails are more likely to reach recipients’ inboxes instead of the spam folder. This reliability increases open and click rates, fostering a more engaged audience.
- Increased Brand Trust and Awareness: Authenticated emails are viewed as more trustworthy, leading to higher interaction rates with your brand and greater willingness to make purchases.
Risks of Poor Email Visibility
Neglecting to implement DMARC and monitor email traffic can have serious consequences for your business, regardless of its size. Poor email deliverability can undermine success, leading to:
- Loss of Customer Trust: Frequent spam folder placements can diminish customer trust, leading to disengagement and loyalty loss.
- Reduced Engagement Opportunities: Unreliable email communications can result in missed sales and interactions if your audience isn’t receiving your messages.
- Increased Vulnerability to Attacks: Without DMARC, your domain is more susceptible to phishing attacks and unauthorized use, putting your brand and customers at risk.
The Importance of DMARC Reports
Implementing DMARC goes beyond security; it also provides valuable insights into your email communications. Here’s why DMARC reports are essential:
- Sender Validation: DMARC helps validate the identity of those sending emails on your behalf, protecting your brand reputation.
- Spoofing Prevention: By identifying and blocking unauthorized senders, DMARC safeguards your brand from misuse by cybercriminals.
- Failure Notifications: DMARC reports notify you of any email delivery failures, allowing for timely resolutions.
How DMARC Works
DMARC operates as an email authentication protocol that requires sender identity validation through SPF (Sender Policy Framework) or DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- SPF and DKIM Setup: Ensure that SPF and DKIM are correctly configured for your domain. SPF specifies authorized mail servers, while DKIM uses cryptographic signatures for verification.
- Creating a DMARC Record: Add a DMARC record to your domain’s DNS settings, outlining your email authentication policy and specifying actions for emails that fail authentication checks (monitor, quarantine, or reject).
- Monitoring DMARC Reports: After activating your DMARC record, begin monitoring the reports to track trends in authentication failures and unauthorized senders.
- Adjusting Policies: Based on your report analysis, you can refine your policies to enhance security and email deliverability. Starting with a “none” policy allows for data gathering before implementing stricter measures.
Benefits of Implementing DMARC
Implementing DMARC not only bolsters security but also yields valuable insights about your email traffic. Key benefits include:
- Improved Deliverability: DMARC can significantly enhance your email deliverability rates by ensuring only legitimate emails are sent from your domain.
- Actionable Insights: DMARC reports offer crucial data on how recipient mail servers treat your emails, guiding necessary adjustments to your email strategy.
- Proactive Security: Regular report reviews help identify potential vulnerabilities in your email systems, enabling preemptive action.
Getting Started with DMARC
Starting with DMARC might seem challenging, but a structured approach can streamline the process. Here are steps to implement DMARC effectively:
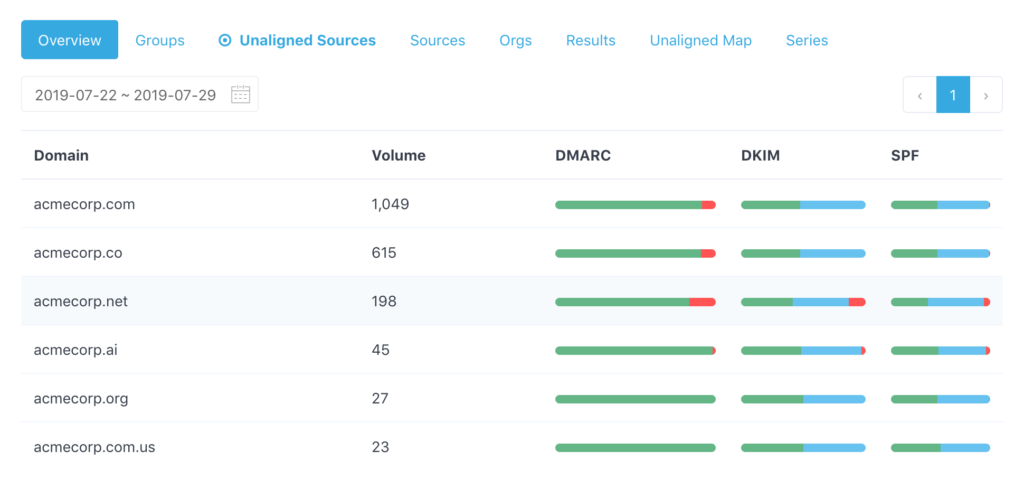
- Understand Your Current Setup: Assess your existing email authentication protocols, ensuring SPF and DKIM are correctly configured.
- Create Your DMARC Record: Draft a DMARC record tailored to your needs, deciding on your policy and including an email address for receiving reports.
- Add the DMARC Record to DNS: Publish your DMARC record in your domain’s DNS settings, enabling receiving mail servers to access your policy.
- Monitor and Analyze Reports: After your DMARC record is live, start monitoring the reports for trends in authentication failures and unauthorized senders.
- Iterate and Optimize: Utilize insights from your reports to adjust DMARC policies. Begin with a lenient policy to gather data, then gradually implement stricter measures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DMARC is a vital tool for organizations aiming to secure their email communications and gain insight into their email activities. By understanding and interpreting DMARC reports, businesses can proactively protect their domains from email fraud while ensuring their messages reach intended recipients. As email threats continue to evolve, robust email authentication strategies like DMARC will be essential for maintaining a secure and trustworthy digital presence.
With the right DMARC approach, you not only protect your brand but also enhance customer trust and engagement. Prioritizing email authentication will be critical as we navigate the challenges of the digital landscape and strive for sustained business growth in 2024.